AI told you the spec requires something. You quoted it. Turns out that requirement doesn't exist.
Welcome to AI hallucinations—the phenomenon where AI confidently makes things up.
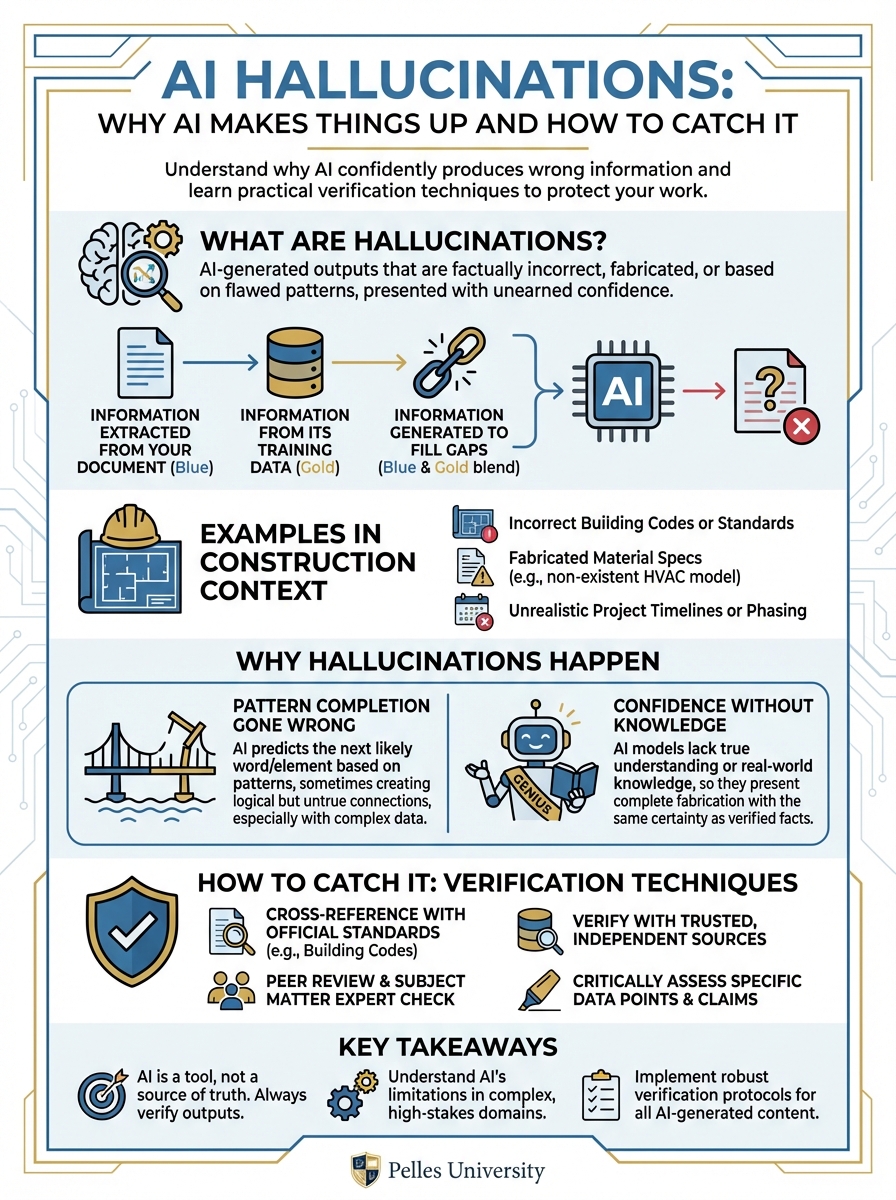
What Are Hallucinations?
AI hallucinations occur when AI generates information that sounds plausible but is factually incorrect. The AI isn't lying—it doesn't know the difference between true and false. It's generating text based on patterns, and sometimes those patterns produce nonsense.
Examples in Construction Context
Hallucinated spec reference: "Per specification Section 23 81 26, Paragraph 3.2.4..." Reality: That paragraph doesn't exist.
Hallucinated requirement: "The specification requires seismic certification to ICC-ES AC156" Reality: The spec says nothing about seismic certification.
Hallucinated manufacturer: "Acceptable manufacturers include Trane, Carrier, and Johnson Controls" Reality: The spec only lists Trane and Carrier.
Hallucinated calculation: "The required airflow is 12,500 CFM based on the schedule" Reality: The schedule shows 10,500 CFM.
Why Hallucinations Happen
Pattern Completion Gone Wrong
AI generates text by predicting what word comes next based on patterns. Sometimes it predicts words that fit the pattern but aren't actually in your documents.
Example: If AI has seen many specs where Section 3.2.4 contains testing requirements, it might reference "Section 3.2.4" even if your spec doesn't have that section.
Confidence Without Knowledge
AI doesn't "know" things—it generates text. It can't distinguish between:
- Information it extracted from your document
- Information from its training data
- Information it generated to fill gaps
Everything comes out with the same confident tone.
Training Data Influence
AI was trained on millions of documents. Sometimes it blends information from training data with information from your specific documents, creating hybrid (wrong) outputs.
How to Catch Hallucinations
Technique 1: Demand Citations
Always ask AI to cite specific sources.
Without citation request: "The specification requires 150% pressure testing"
With citation request: "The specification requires 150% pressure testing (Section 22 05 00, Paragraph 3.4.2)"
Now you can verify: Does Section 22 05 00, Paragraph 3.4.2 actually say this?
Technique 2: Spot Check
For any AI output, randomly verify 3-5 facts against source documents.
Process:
- Pick items at random from the AI output
- Find the cited source location
- Verify the claim matches the source
- If errors found, increase verification
If spot checking reveals errors, don't trust the rest without full verification.
Technique 3: Cross-Reference
Have AI answer the same question in different ways and compare.
First prompt: "What testing requirements are in Section 23 21 13?"
Second prompt: "List every paragraph in Section 23 21 13 that mentions testing"
If the answers conflict, something's wrong.
Technique 4: Ask for Uncertainty
Tell AI to flag when it's uncertain.
Prompt addition: "If you're not certain about any item, mark it with [VERIFY] so I know to check it manually."
This won't catch all hallucinations, but it catches some.
Technique 5: Structured Output
Request structured output that's easier to verify.
Unstructured (hard to verify): "The spec has several testing requirements including pressure testing, cleaning, and inspection..."
Structured (easy to verify):
| Requirement | Section | Paragraph | Quote |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure test | 23 21 13 | 3.4.1 | "Test at 150 PSI for 2 hours" |
Structured output forces AI to commit to specifics you can check.
High-Risk Situations
When to Verify Everything
Some situations require 100% verification:
- Contract language: Every clause, every reference
- Pricing backup: Every quantity, every rate
- Legal/compliance items: Every requirement, every citation
- Safety-related content: No exceptions
When Spot Checking Is OK
Lower-risk situations where spot checking may be sufficient:
- Internal summaries: Meeting notes, project updates
- First drafts: RFIs, letters (you'll review anyway)
- Research questions: General information gathering
When to Skip AI
Some tasks shouldn't use AI at all:
- Novel legal questions: Get actual legal advice
- Safety determinations: Require qualified professionals
- Final documents: Human review always required
Building Verification Habits
Make It Part of the Process
Verification shouldn't be optional. Build it into your workflow:
- AI generates output
- Human spot checks citations
- If errors found, full review
- If clean, proceed with normal review
Track Error Rates
Keep a simple log:
- How many AI outputs reviewed?
- How many had errors?
- What types of errors?
This tells you how much to trust AI for different tasks.
Adjust by Task Type
Some tasks have higher hallucination risk:
Higher risk:
- Specific numbers (quantities, dimensions)
- Exact quotes from documents
- Reference citations (section numbers)
- Manufacturer names and model numbers
Lower risk:
- General summaries
- Process explanations
- Format and structure
- Common industry practices
When AI Gets It Wrong
The Verification Safety Net
AI hallucinations are inevitable. The safety net is verification. If incorrect information gets through, it usually means the verification step was missed. Success with AI depends on this final check.
Document the Error
Note what went wrong:
- What did AI claim?
- What was the reality?
- Why wasn't it caught?
Improve the Process
Update your verification approach based on the error type.
Move On
Errors happen. The goal is reducing them, not eliminating them entirely.
Verification Checklist
Before using any AI output for important work:
- Did AI cite specific sources?
- Have I verified at least 3-5 citations?
- Do the numbers make sense?
- Does this match my industry knowledge?
- Would I be comfortable if this were audited?
If you can't check all these boxes, more verification is needed.
What's Next
Understanding hallucinations protects you from AI mistakes. The next step is learning where AI fits in your workflow—which tasks benefit from AI and which don't.
TL;DR
- AI hallucinations are confident-sounding but wrong outputs
- They happen because AI predicts text patterns, not facts
- Always demand citations you can verify
- Spot check 3-5 items from any AI output
- High-risk work (contracts, pricing, safety) needs 100% verification
- Track error rates to calibrate your trust level