You just pasted a contract into ChatGPT. Where did that data go? Who can see it? Could it show up somewhere else?
These are real questions with real implications for contractors.
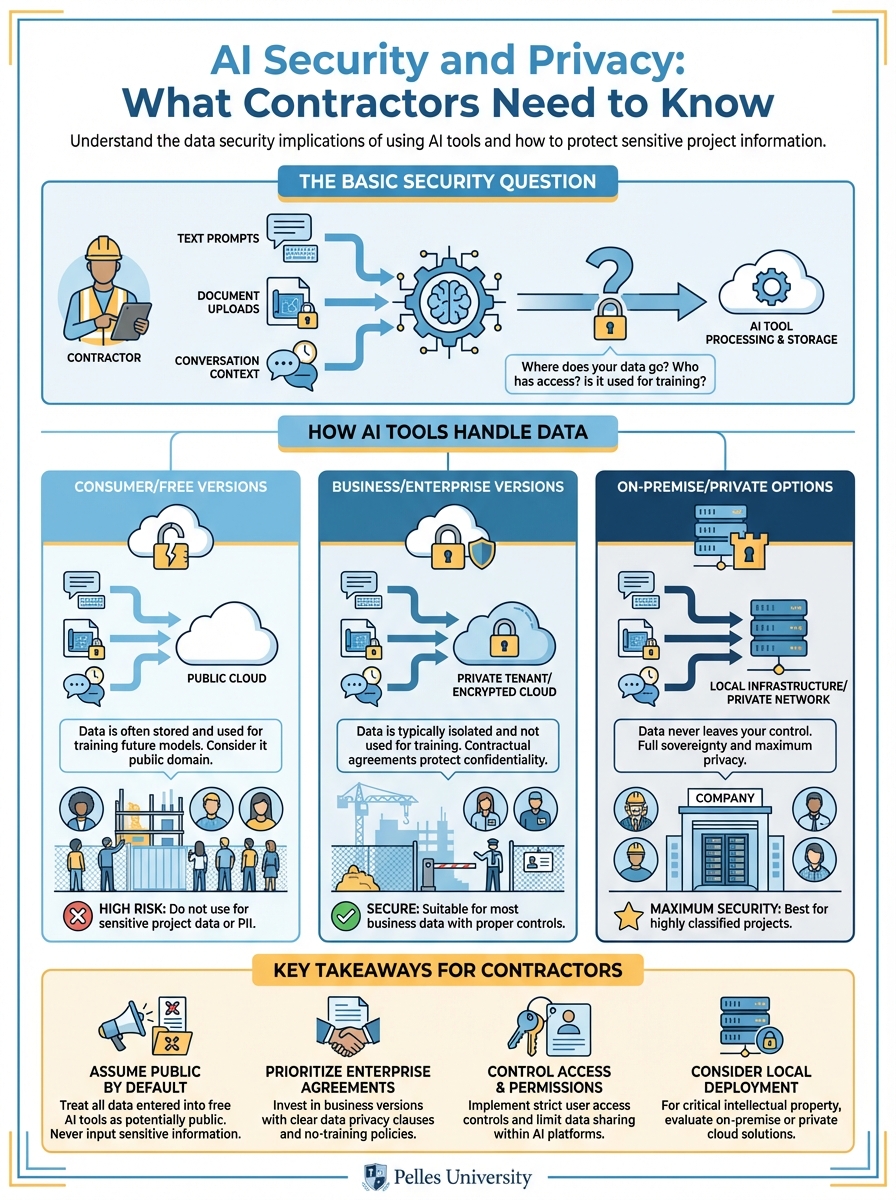
The Basic Security Question
When you use AI tools, you're sending data to external systems. That data typically includes:
- The text you input (prompts)
- Documents you upload
- The context of your conversation
Where this data goes and how it's used varies dramatically by tool and plan.
How AI Tools Handle Data
Consumer/Free Versions
Most free AI tools (like ChatGPT free tier):
- May use your data for training: Your inputs could help train future AI models
- Data is stored: Conversations are saved, at least temporarily
- Limited privacy controls: You're trading privacy for free access
- Terms can change: Read the current terms, not old assumptions
Implication: Don't put confidential information into free AI tools.
Business/Enterprise Versions
Paid business versions typically offer:
- No training on your data: Your inputs stay private
- Data retention controls: You control how long data is kept
- Compliance certifications: SOC 2, GDPR, etc.
- Admin controls: Who can access what
Implication: If you need to use AI with sensitive data, pay for a business tier.
On-Premise/Private Options
Some organizations deploy AI internally:
- Data never leaves your network: Maximum control
- You manage everything: Including security
- Higher cost and complexity: Requires IT resources
Implication: For highly sensitive applications, consider private deployment.
What Data Should Never Go Into Public AI
Absolutely Never
- Social Security Numbers
- Bank account information
- Passwords or credentials
- Personal health information
- Personal contact information of others
These are non-negotiable regardless of the AI tool.
Probably Never (Without Business-Tier Protection)
- Contract pricing and terms
- Client confidential information
- Bid strategies and pricing
- Employee personal information
- Financial details
Use business-tier tools with proper data protection for these.
Exercise Caution
- Project names and locations
- Client names
- Proprietary processes
- Internal communications
Consider whether this information could cause harm if exposed.
Contract Implications
NDAs and Confidentiality
Many contracts include confidentiality provisions. Using AI might violate them.
Typical NDA language: "Contractor shall not disclose Confidential Information to any third party..."
Question: Is an AI service a "third party"?
Safe answer: Yes, treat it as one unless you have explicit permission.
Data Handling Requirements
Some contracts specify how data must be handled.
Example requirements:
- Data must be stored in approved systems only
- Data must not leave the country
- Data must be encrypted at rest and in transit
Question: Does your AI tool comply?
When in Doubt
- Read your contracts
- Ask your client
- Get written approval for AI use
- Document what tools you're using
Practical Data Protection
Sanitization Techniques
Remove sensitive information before using AI:
Before:
Review this contract between ABC Hospital and XYZ Mechanical
for the $4.2M HVAC renovation project...
After:
Review this contract between [Client] and [Contractor]
for the [description redacted] project...
You can still get useful analysis without exposing specifics.
Use Placeholder Data
Replace real information with placeholders:
- Names → [Party A], [Party B]
- Amounts → [Amount], [Percentage]
- Dates → [Date 1], [Date 2]
- Locations → [Location]
The AI can still analyze structure and terms.
Separate Sensitive from Non-Sensitive
Not everything is sensitive. Categorize your data:
Non-sensitive (probably OK):
- Public specifications
- Published standards
- General industry practices
- Non-proprietary processes
Sensitive (use protection):
- Pricing
- Client information
- Contract terms
- Internal strategies
Choosing Secure AI Tools
Questions to Ask
- Where is data stored? What country/region?
- Is data used for training? Can you opt out?
- How long is data retained? Can you delete it?
- What certifications exist? SOC 2? ISO 27001?
- Who can access your data? Employees? Contractors?
- What happens in a breach? Notification? Liability?
Red Flags
- No clear privacy policy
- Can't answer security questions
- No business/enterprise tier
- No compliance certifications
- Data retention you can't control
Green Flags
- Clear, readable privacy policy
- Business tier with enhanced privacy
- No training on user data (opt-out available)
- Compliance certifications
- Data deletion capabilities
- Transparent about data handling
Building Secure Practices
Policy First
Before widespread AI use, establish:
- What tools are approved?
- What data can be used with AI?
- Who approves exceptions?
- How do we document AI use?
Training Second
Make sure your team knows:
- What's allowed and what isn't
- How to sanitize data
- When to ask questions
- Where to report concerns
Monitoring Third
Keep track of:
- What tools are being used?
- What data is being processed?
- Any incidents or concerns?
When AI Finds Something Concerning
If AI reveals a potential problem (contract issue, compliance concern, etc.):
- Don't panic: AI might be wrong
- Verify first: Check the source documents
- Consult appropriate people: Legal, management, etc.
- Document the finding: What was found, how, when
- Take appropriate action: Based on verified information
Project-Specific Considerations
Bid Documents
- Pre-award: Be careful with pricing strategies
- Public bids: Less sensitive (publicly available eventually)
- Private bids: More caution needed
Contracts
- Higher sensitivity
- Consider sanitization
- Use business-tier tools
Project Documents
- Varies by document type
- Public specs: Lower risk
- Internal correspondence: Higher risk
Financial Information
- Always sensitive
- Maximum protection
- Consider not using AI at all
What's Next
Understanding security lets you use AI responsibly. With these basics covered, you're ready to explore specific AI applications for your construction workflows.
TL;DR
- Free AI tools may use your data for training—don't put confidential info in them
- Business-tier tools offer better privacy protection
- Contracts may require data protection that affects AI use
- Sanitize sensitive data before using AI (replace names, amounts, etc.)
- Establish policies before widespread AI adoption
- When in doubt, ask before putting data into AI